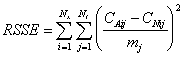
| [TOC] | 4.2 Measures of Performance | [Prev. Page] | [Next Page] |
This chapter compares numerical and analytical solutions both qualitatively and quantitatively. Qualitative analysis involves a visual comparison of numerical and analytical solutions. Quantitative analysis uses mathematical means to measure the difference between numerical and analytical solutions. There are many ways to quantitatively measure the error in a numerical simulation. Some of these methods include: maximum absolute error, sum of absolute error, sum of squared error, relative sum of square error, and mass balance error.
Choice of a proper quantitative measurement of error is an important task. Sometimes the use of certain methods is inappropriate for the numerical model. For example, the numerical described in this thesis is mass conservative by definition, computing the mass balance error would be meaningless. Also, other methods may yield identical results. Numerical experimentation with this model has shown that error calculations using absolute and relative measurement yield qualitatively similar results.
This thesis uses the Relative Sum of Square Error (RSSE) to quantify the difference between numerical and analytical solutions. The definition of RSSE for this thesis is:
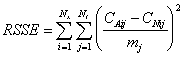 |
(4.1) |
With: RSSE = relative sum of square error Nx = number of nodes in the aquifer Nt = number of time intervals in the simulation CAij = analytical concentration at node i, time j CNij = numerical concentration at node i, time j mj = maximum analytical concentration in aquifer at time j
This method yields the sum of squared errors at every node in the aquifer for every timestep in the simulation. The errors are normalized by the maximum analytical concentration at each timestep. Numerical experimentation has shown that this computation yields similar results as other methods such as the maximum absolute error and sum of squared errors.
| [Home] | [Table of Contents] | [Prev. Page] | [Next Page] |
| A Two Dimensional Numerical Model for Simulating the
Movement and Biodegradation of Contaminants in a Saturated Aquifer © Copyright 1996, Jason E. Fabritz. All Rights Reserved. |
|||